|
|
Sato S and Mukai M, et al. Significance of occult neoplastic cells on tumor metastasis:
a case report of gastric cancer. Diagnostic Pathology 5: 14-18, 2010. |
|
Mukai M, et al. Efficacy of 5FU/LV+CPT-11 as the 1st -line postoperative adjuvant
chemotherapy in patients with stage IIIa colorectal cancer.
Oncol Rep 22: 621-629, 2009. |
|
Mukai M, et al. Comparison of QOL and adverse events for postoperative adjuvant
chemotherapy in outpatients with node-positive colorectal or gastric cancer.
Oncol Rep 21: 1061-1066, 2009. |
|
Ito I, Mukai M, et al. Comparison between intravenous and oral postoperative
adjuvant immunochemotherapy in patients with stage III colorectal cancer.
Oncol Rep 2008; 20; 1521-1526. |
|
Ito I, Mukai M, et al. Comparison between intravenous and oral postoperative
adjuvant immunochemotherapy in patients with stage II colorectal cancer.
Oncol Rep 2008; 20: 1189-1194. |
|
Mukai M, et al. Sensitivity to CPT-11 and platinum derivatives of stage II/III
node-positive gastric cancer with occult neoplastic cells in lymph node
sinuses.
Ann Cancer Res Thera 2007; 13: 22-26. |
|
Mukai M, et al. Sensitivity to CPT-11 and platinum derivatives of stage I/II
node-negative breast, lung and gastric cancer with occult neoplastic cells
in lymph
node sinuses.Oncol Rep 2007; 18: 33-39.
|
|
Mukai M, et al. Local recurrence and occult neoplastic cells in the dissected
perinodal fat around the lymph nodes in patients with curatively resected
primary
colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 2007; 17: 1365-1369.
|
|
Hoshikawa T, Mukai M, et al. Pelvic recurrence after Miles’ operation for
anastomotic recurrence in a patient with stage I rectal cancer invading
the proper
muscle layer: Case report. Oncol Rep 2007; 17: 743-746.
|
|
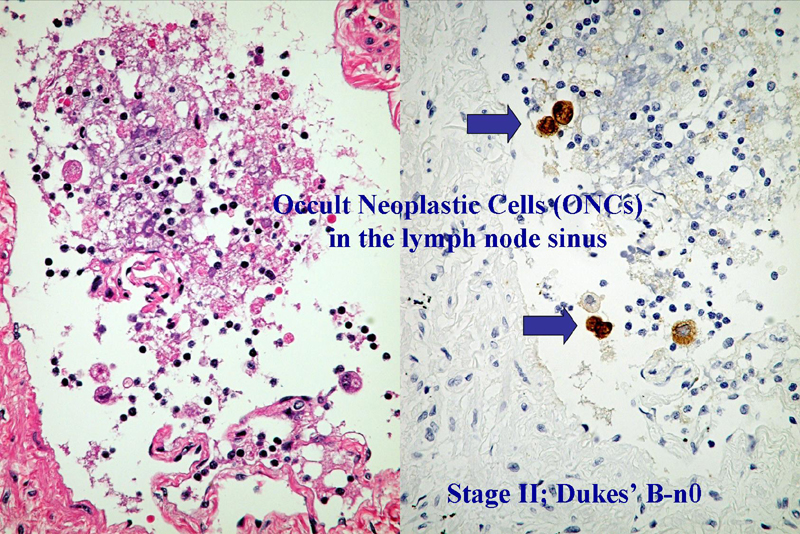
Mukai M, et al. Sensitivity of CPT-11 and platinum derivatives of stage II/Dukes’ B
colorectal cancer with occult neoplastic cells in lymph node sinuses.
Oncol Rep 2007; 17: 1045-1050. |
|
Mukai M, et al. Sensitivity of CPT-11 and platinum derivatives of stage III/Dukes’ C
colorectal cancer with occult neoplastic cells in lymph node sinuses.
Oncol Rep 2007; 17: 1027-1032. |
|
Mukai M, et al. Alternating hepatic arterial infusion and systemic chemotherapy in
patients of stage IV colorectal cancer with synchronous liver metastasis.
Oncol Rep 2006; 16: 865-870.
|
|
Mukai M, et al. Prospective study on the recurrence/metastasis of stage II/III colorectal
cancer and gastric cancer associated with occult neoplastic cells in lymph node sinuses:
Three-year interim results. Oncol Rep 2006; 16: 405-410. |
|
Hasegawa S, Mukai M, et al. Long-term survival and tumor 5-FU sensitivity in
patients with stage IV colorectal cancer and peritoneal dissemination.
Oncol Rep 2006; 15: 1185-1190. |
|
Tajima T, Mukai M, et al. Predicting recurrence and metastasis of primary esophageal
cancer with or without lymph node metastasis.
Oncol Rep 2006; 15: 809-814.
|
|
Mukai M, et al. Recurrence and 5-FU sensitivity of stage I/II node-negative
gastric, breast and lung cancer with occult neoplastic cells in lymph node
sinuses.
Oncol Rep 2006; 15 : 815-820. |
|
Muramatsu T, Mukai M, et al. Clinical usefulness of serum and immunohistochemical
markers in patients with stage Ia and Ic ovarian cancer.
Oncol Rep 2005; 14: 861-865. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Recurrence and 5-FU sensitivity of stage II/III
node-positive gastric cancer with occult neoplastic cells in lymph node
sinuses.
Oncol Rep 2005; 14 : 1505-1510. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Recurrence and 5-FU sensitivity of stage II/Dukes’
B colorectal cancer with occult neoplastic cells in lymph node sinuses.
Oncol Rep 2005; 14: 1171-1176. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Recurrence and 5-FU sensitivity of stage III/Dukes’
C colorectal cancer with occult neoplastic cells in lymph node sinuses.
Oncol Rep 2005; 14: 1165-1169. |
|
Masaya Mukai. Occult neoplastic cells and malignant micro-aggregates
in lymph node sinuses: Review and hypothesis.
Oncol Rep 2005; 14: 173-175. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Predicting recurrence and metastasis of Dukes’A
primary colorectal cancer with or without proper muscle invasion.
Oncol Rep 2004; 12: 1305-1308. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Predicting recurrence and metastasis of stage II/Dukes’B
colorectal cancer without lymph node metastasis.
Oncol Rep 2004; 12: 1127-1130. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Predicting recurrence and metastasis of stage III/Dukes’C
colorectal cancer with lymph node metastasis.
Oncol Rep 2004; 12: 1301-1304. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Predicting the recurrence/metastasis of stage I and II
breast cancer without lymph node metastasis.
Oncol Rep 2004; 12: 745-748. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Predicting the recurrence/metastasis in stage II and III
breast cancer with lymph node metastasis.
Oncol Rep 2004; 12: 303-306.
|
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Accurary of criteria for predicting the recurrence and
metastasis in stage Ⅱ and Ⅲ gastric cancer with lymph node metastasis.
Oncol Rep 2004; 12: 59-62. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Accurary of criteria for predicting the recurrence
and
metastasis of stage Ⅰ and Ⅱ gastric cancer without lymph node metastasis.
Oncol Rep 2004; 12:63-66. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Occult neoplastic cells in the lymph node sinuses and
recurrence in patients with primary breast, lung, esophageal and gastric
cancer.
Oncol Rep 2004;11: 81-84. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Efficacy of postoperative adjuvant oral immunochemotherapy in patients with Dukes’ B colorectal cancer.
Ann Cancer Res Therap 2003;11:201-214 . |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Efficacy of postoperative adjuvant oral immunochemotherapy in
patients with Dukes’C colorectal cancer.
Ann Cancer Res Therap 2003;11:215-229. |
|
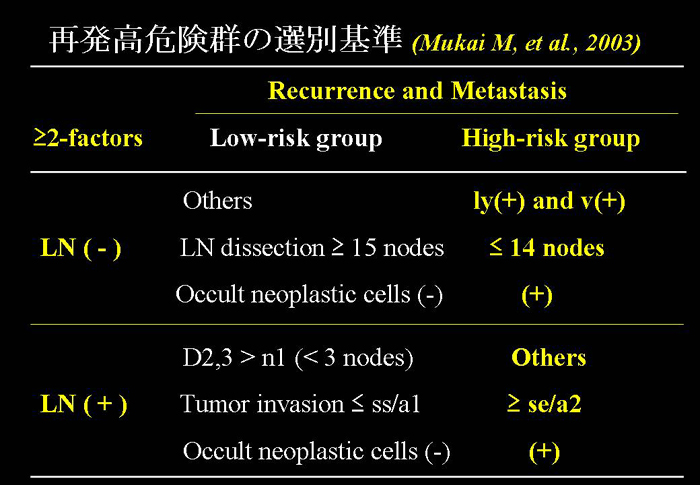
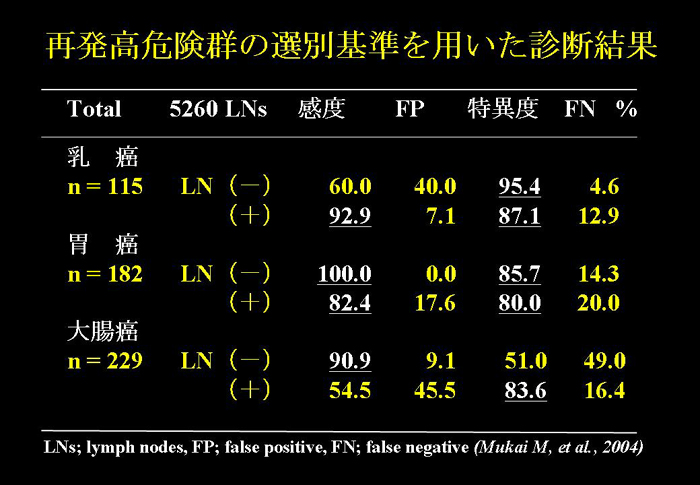
Masaya Mukai, et al. Selection criteria for high risk and low risk groups
of recurrence
and metastasis in patients with primary colorectal cancer.
Oncol Rep 10: 1753-1758, 2003. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Correlation between occult neoplastic cells in the lymph node
sinuses and recurrence in patients with curatively resected Dukes’ B colorectal
cancer.
Oncol Rep 2003; 10: 1177-1181. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Correlation between occult neoplastic cells in the lymph node
sinuses and recurrence in patients with Dukes’ C colorectal cancer.
Oncol Rep 2003; 10: 1165-1169. |
|
Masaya Mukai, et al. Improvement of 10-year survival by Japanese radical lymph node dissection in patients with Dukes’ B and C colorectal cancer: a 17-year retrospective study.
Oncol Rep 2003; 10: 927-934.
他、多数論文より。
|